 Maharashtra HSC Chemistry Exam 2026 LIVE
Maharashtra HSC Chemistry Exam 2026 LIVEMaharashtra HSC Chemistry Exam 2026: The Maharashtra HSC Chemistry exam is scheduled for February 18, 2026, from 11 AM to 2 PM. This is the part of the Class 12 board tests taking place from February 10 to March 11 this year. If you are appearing for Chemistry, keep reading! In this live blog, we are providing the most important questions you should focus on, how marks are distributed across chapters, and simple revision tips from experts to help you improve your score. Stay tuned for Maharashtra HSC Chemistry exam updates, focus on smart preparation, and get ready to write your best paper yet. We will be providing the Chemistry answer key along with student reviews through the same live blog on Wednesday, February 18.
Maharashtra HSC Chemistry Exam 2026: Quick Facts
Check below some of the facts and important details related to the Maharashtra HSC Chemistry Exam 2026:
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Chemistry exam date | February 18, 2026 (1 day to go) |
Exam time | 11:00 AM to 2:00 PM |
Maximum marks | 70 Marks |
Total No. of sections | Section A, B, C, and D |
Total No. of MCQs | 10 MCQs in Section A |
Marks Distribution |
|
Also Read:
Maharashtra HSC Physics Answer Key 2026
So, as the Maharashtra HSC Chemistry exam on February 18, 2026, is getting closer and closer, remember that this is your chance to give your best. Instead of stressing about how tough the paper might be, think about how you can use the three hours wisely. Attempt the questions you are most confident about first. Keep your answers neat and to the point. This exam is important, yes, but it is also manageable. You’ve got this! Any latest update pertaining to the HSC Chemistry exam shall be provided through the live blog below.
Also read |
JEE Main Toppers List 2026 LIVE Updates
Maharashtra HSC Chemistry Exam 2026 LIVE Updates
07 30 PM IST - 17 Feb'26
Chemical Kinetics Question with Solution
Q: 60% of the reactant decomposes in 45 minutes in a first order reaction. Calculate the half life period of the reaction.
Given:
60% of the reactant decomposes in 45 minutes. Therefore, 40% of the reactant remains.Initial concentration = a
Amount remaining after 45 min = 0.4a
Hence, the half-life of the reaction is 34.14 minutes.
06 30 PM IST - 17 Feb'26
Some Important 4-Mark Questions from Chemical Thermodynamics
Q: (a) Define the following terms:
(i) Enthalpy of atomization
(ii) Extensive properties(b) Write the mathematical statement of the first law of thermodynamics for the following processes:
(i) Isothermal process
(ii) Adiabatic processQ: (a) Define the following terms:
(i) Bond enthalpy
(ii) Enthalpy of ionization(b) Calculate the standard enthalpy of the reaction:
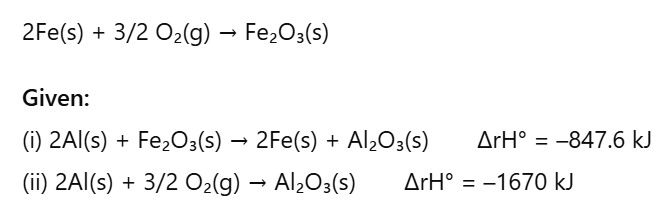
Q: (a) Classify the following into intensive and extensive properties. Pressure, volume, mass, temperature.
(b) Define a state function and write two examples of it.
06 00 PM IST - 17 Feb'26
Some Important 3-Mark Questions from Chemical Thermodynamics
Q: (a) Define an isolated system.
(b) Three moles of an ideal gas are expanded isothermally from 15 dm³ to 20 dm³ against a constant external pressure of 1.2 bar. Calculate the amount of work done in joules.
Q: (a) Define enthalpy of fusion.
(b) Derive an expression for the maximum work done by a system.Q: (a) Derive the expression: ΔH = ΔU + PΔV.
(b) Write the relationship between heat (Q) and change in internal energy (ΔU) for an isochoric process.Q: (a) Define standard enthalpy of formation.
(b) Derive the relationship between the standard enthalpy of reaction and the standard enthalpies of formation of reactants and products for the reaction:aA + bB → cC + dD.
05 30 PM IST - 17 Feb'26
Some Important 2-Mark Questions from Chemical Thermodynamics
- Define the terms: (i) Standard enthalpy of combustion (ii) Enthalpy of sublimation.
- State and explain Hess's law of constant heat summation.
- Write the features of reversible processes.
05 00 PM IST - 17 Feb'26
Some Important 1-Mark Questions from Chemical Thermodynamics
- An intensive property amongst the following is………….
- The work done in the dm3bar when 200 mL of ethylene gas and 150 mL of HCl gas were allowed to react at 1 bar pressure is….
- Write the expression to calculate the maximum work done when 1 mole of an ideal gas expands isothermally and reversibly from V1 to V2.
- Write the mathematical relation between ∆H and ∆U during the formation of one mole of CO2 under standard conditions.
04 30 PM IST - 17 Feb'26
Important Order-Based Question from Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Arrange the following in increasing order of the property mentioned:
(i) HOCl, HClO2, HClO3, HClO4 (acidic strength)
(ii) MF, MCl, MBr, MI (ionic character)
(iii) HF, HCl, HBr, HI (thermal stability)
04 00 PM IST - 17 Feb'26
Some more important 4-mark questions for HSC Chemistry
Q: Convert the following:
(i) Acetaldehyde to isopropyl alcohol.
(ii) Cumene to phenol.
(iii) Anisole to phenol.
Write two uses of neon.Q: Define:
(i) Extensive and intensive properties.
(ii) Isobaric and adiabatic processes.
What are enzymes?
Write the atomic numbers of transuranium elements.Q: A solid element has a cubic lattice with edge length 400 pm and density 6.25 g mL⁻¹. The atomic mass of the element is 60. Predict the type of cubic lattice.
Define nanoscience.
Write the chemical reaction for the preparation of polyacrylonitrile.Q: Derive the relation between the half-life period and the rate constant for a first-order reaction.
Write the net cell reaction during the discharging of a lead accumulator.
Draw the structure of peroxymonosulphuric acid.Q: Mention the number of unpaired electrons and geometry of the following complexes:
Convert the following:
(i) [NiCl₄]²⁻
(ii) [Ni(CN)₄]²⁻
(a) Ethanenitrile into ethanal.
(b) Cyclohexane into adipic acid.03 30 PM IST - 17 Feb'26
What is osmotic pressure?
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to stop the flow of solvent molecules into it through a semipermeable membrane. It is a colligative property and depends only on the number of solute particles present in the solution.
Mathematically, osmotic pressure is given by the equation: π=CRT
Where,
π = osmotic pressure
C = molar concentration of solution
R = gas constant
T = temperature in KelvinIt is usually expressed in atmospheres (atm).
03 00 PM IST - 17 Feb'26
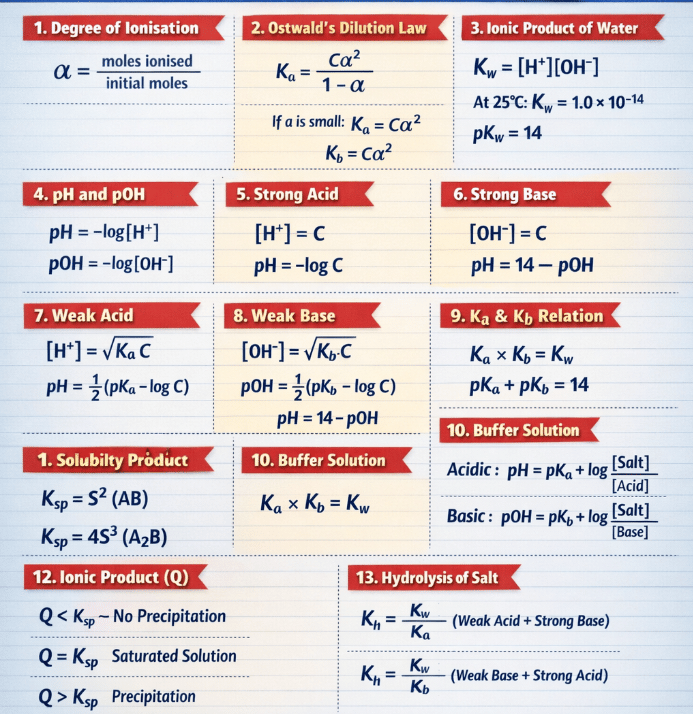
Ionic Equilibrium: All Important Formulas to Remember
02 30 PM IST - 17 Feb'26
Some Important 4-Mark Questions from Ionic Equilibrium
Q: (a) Derive the equation
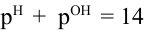
(b) Distinguish between strong electrolyte and weak electrolyte
Q: (a) Explain the amphoteric nature of water.
(b) Define i) Solubility product ii) Hydrolysis of salt
02 00 PM IST - 17 Feb'26
Some Important 3-Mark Questions from Ionic Equilibrium
- Define buffer solution. Explain its types.
- Write one application for each of the following buffers.
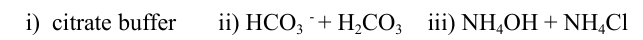
- Derive the equation that implies that the degree of dissociation of a weak acid is inversely proportional to the square root of its concentration.
01 30 PM IST - 17 Feb'26
Some Important 2-Mark Questions from Ionic Equilibrium
- Define the following terms i) pH ii) pOH 5) Define molar solubility. Write its unit.
- Explain Ostwald’s dilution law for weak acids.
- Explain Ostwald’s dilution law for weak bases.
- Write any four applications of buffer solution
01 00 PM IST - 17 Feb'26
Some Important 1-Mark Questions from Ionic Equilibrium
- What is the percentage dissociation of 0.1 M Solution of acetic acid?
- In the biochemical system, the pH of blood in our body is maintained due to the following buffer
- If ‘IP’ is the ionic product and ‘ksp’ is the solubility product, precipitation of the compound will occur under the condition when.
- Write the name of buffer which is used to maintain pH of 8 to 10 for precipitation of cations of III A group in qualitative analysis
- Write the solubility product of sparingly soluble salt Bi2S3
- What is the pOH if the hydrogen ion concentration in solution is
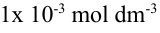
12 30 PM IST - 17 Feb'26
Applied Chemistry Expected Weightage for 2026
Topic Number Chapter Name Weightage Distribution without Options Weightage Distribution with Options Applied Chemistry Biomolecules 3-4 marks 4-5 marks Introduction to Polymer Chemistry 3-4 marks 4-5 marks Green Chemistry and Nano Chemistry 3-4 marks 4-5 marks 12 00 PM IST - 17 Feb'26
Organic Chemistry Expected Weightage for 2026
Topic Number Chapter Name Weightage Distribution without Options Weightage Distribution with Options Organic Chemistry Halogen Derivatives 5-6 marks 6-7 marks Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers 4-5 marks 6-7 marks Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids 5-6 marks 7-8 marks Amines 3-4 marks 4-5 marks 11 30 AM IST - 17 Feb'26
Inorganic Chemistry Expected Weightage for 2026
Topic Number Chapter Name Weightage Distribution without Options Weightage Distribution with Options Inorganic Chemistry Elements of Groups 16, 17, & 18 5-6 marks 7-8 marks Transition & Inner Transition Elements 5-6 marks 7-8 marks Coordination Compounds 5-6 marks 7-8 marks 11 00 AM IST - 17 Feb'26
Physical Chemistry Expected Weightage for 2026
Topic Number Chapter Name Weightage Distribution without Options Weightage Distribution with Options Physical Chemistry Solid State 3-4 marks 5-6 marks Solutions 4-5 marks 5-6 marks Ionic Equilibrium 4-5 marks 5-6 marks Chemical Thermodynamics 5-6 marks 7-8 marks Electrochemistry 5-6 marks 7-8 marks Chemical Kinetics 4-5 marks 5-6 marks 10 30 AM IST - 17 Feb'26
How to Download PYQs for Chemistry?
Step 1: Go to the official website of the Maharashtra HSC Board at mahahsscboard.in.
Step 2: Once you are on the homepage, look for the student section. Find the link related to previous year question papers or model question papers and click on it.
Step 3: Select Class 12 (HSC) from the list of classes, then choose Chemistry as your subject.
Step 4: Now, select the specific year for which you want to access the question paper.
Step 5: Check that you have selected the correct class, subject, and year. Then proceed to download the Maharashtra HSC Chemistry previous year question paper in PDF format.
Step 6: Save the file on your device and start solving it to improve your speed, accuracy, and overall exam readiness.
10 00 AM IST - 17 Feb'26
Maharashtra HSC Chemistry Exam 2026 Last Day Reminder!
The Chemistry paper will be conducted in the morning session from 11:00 AM to 2:00 PM. Students are advised to reach the exam centre at least 30 minutes before 11:00 AM, preferably by 10:30 AM to avoid last-minute rush.
08 37 AM IST - 17 Feb'26
HSC Chemistry Exam 2026 Tomorrow: Is the question paper leaked?
Multiple rumours have been circulating onthe Maharashtra HSC paper leak. There were rumours on HSC Physics paper leak as well. Students must note that there were no instances of paper leak reported officially by the board or Police Department. There is no scope for the leak of Chemistry paper as well.
08 00 AM IST - 17 Feb'26
Maharashtra HSC Chemistry Exam 2026 Last Day Prep Tips
- Do not rely on any YouTube video claiming it has the exact question paper.
- Ignore leaked paper rumors and focus only on your syllabus.
- Revise important formulas, reactions, and definitions once more.
- Go through previous years’ Maharashtra HSC Chemistry question papers.
- Focus more on high-weightage chapters instead of new topics.
- Do not start any completely new chapter today.
- Practice writing balanced chemical equations neatly.
- Revise diagrams like electrochemical cells and organic mechanisms.
- Read textbook in-text and back exercise questions carefully.
- Sleep on time and keep your mind calm before the exam.
07 40 AM IST - 17 Feb'26
SN1 vs SN2 Reaction
SN1
SN2
Two-step
One-step
Forms carbocation
No carbocation
Rate depends on 1 reactant
Rate depends on 2 reactants
07 20 AM IST - 17 Feb'26
Molarity vs Molality
Molarity (M): Moles of solute per litre of solution. Depends on temperature.
Molality (m): Moles of solute per kg of solvent. Does not depend on temperature.07 00 AM IST - 17 Feb'26
Organic Chemistry Rapid Fire Questions for Revision
- Aldehyde group is –CHO at which position?
- SN2 reaction: one-step or two-step?
- Markovnikov rule: H adds to carbon with more or fewer hydrogens?
- Nucleophile: electron-rich or electron-deficient?
- Ketone: carbonyl at end or middle of chain?
06 40 AM IST - 17 Feb'26
Inorganic Chemistry Rapid Fire Questions for Revision
- Ligand attached through two or more donor atoms is called?
- Lanthanoids belong to which series?
- Complex salt - completely dissociates in water or not?
- Heteroleptic complex contains how many types of ligands?
- Difference between allotropy and isomerism?
06 20 AM IST - 17 Feb'26
Physical Chemistry Rapid Fire Questions for Revision
- Moles of solute per litre of solution is called?
- Molecularity of a reaction is always theoretical or experimental?
- Strong electrolyte - completely or partially ionizes?
- What does the rate of reaction depend on in an SN1 reaction?
- Which cell converts chemical energy into electrical energy?
06 00 AM IST - 17 Feb'26
Maharashtra HSC Chemistry Exam 2026 Hall Ticket
Check your Hall Ticket now. Ensure the photo and signature are clear. Keep it in your exam bag with a valid ID.
05 00 AM IST - 17 Feb'26
Important Numerical from Solutions Chapter
Question: A mixture of benzene and toluene contains 30% by mass of toluene. At 30°C, vapour pressure of pure toluene is 36.7 mmHg and that of pure benzene is 118.2 mmHg. Assuming that the two liquids form ideal solution, calculate partial pressure of each constituent in the above solution at 30°C.
Answer:
Given:
Mass % of toluene = 30%
Mass % of benzene = 70%Vapour pressure of pure toluene (P°ₜ) = 36.7 mmHg
Vapour pressure of pure benzene (P°ᵦ) = 118.2 mmHgTemperature = 30°C
Step 1: Assume total mass of solution = 100 g
Mass of toluene = 30 g
Mass of benzene = 70 gStep 2: Calculate number of moles
Molar mass:
Benzene (C₆H₆) = 78 g/mol
Toluene (C₇H₈) = 92 g/molMoles of toluene:
nₜ = 30 / 92 = 0.326 mol
Moles of benzene:
nᵦ = 70 / 78 = 0.897 mol
Step 3: Calculate mole fraction
Total moles = 0.326 + 0.897 = 1.223 mol
Mole fraction of toluene:
Xₜ = 0.326 / 1.223 = 0.267
Mole fraction of benzene:
Xᵦ = 0.897 / 1.223 = 0.733
Step 4: Apply Raoult’s Law
Raoult’s Law:
P = X × P°
Partial pressure of toluene:
Pₜ = 0.267 × 36.7
Pₜ = 9.80 mmHgPartial pressure of benzene:
Pᵦ = 0.733 × 118.2
Pᵦ = 86.64 mmHgFinal Answer
Partial pressure of toluene = 9.80 mmHg
Partial pressure of benzene = 86.64 mmHg
03 00 AM IST - 17 Feb'26
Important Questions of Ionic Equilibrium
- Explain ‘common ion effect’ with example.
- Derive Ostwald’s dilution law for weak acid. Obtain relation between solubility product and its solubility for Al(OH)3.
- Write the name of buffer which is used to maintain pH of 8 to 10 for precipitation of cations of III A group in qualitative analysis
- If ‘S’ is solubility in mol dm and ksp is the solubility product. Then write the relation between them for the CaF2 and BaSO4
02 00 AM IST - 17 Feb'26
Important Questions of Solid State
- Define a unit cell.
- Which colour is shown by NaCl crystal due to formation of F-centre?
01 00 AM IST - 17 Feb'26
Important Questions of Organic Chemistry
- Explain optical activity in 2-chlorobutane.
- Write structural formula for methyl vinyl ether.
- Explain Aldol condensation reaction of ethanal.
- Write note on Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
12 00 AM IST - 17 Feb'26
Important Questions of Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Write full name of DDT.
- What are antacids? Give one example.
- Differentiate between analgesics and antipyretics.
- What are antiseptics and disinfectants? Explain with suitable examples.
11 00 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Important Questions of Chemical Thermodynamics
- State whether the reaction is spontaneous or non-spontaneous if ΔH = 50 kJ and ΔS = –130 J K⁻¹ at 250 K.
- State whether entropy change is positive or negative: (i) Melting of ice (ii) Vaporisation of a liquid
10 40 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Important Questions of Coordination Compounds
- Explain the formation of [Co(NH₃)₆]³⁺ ion on the basis of Valence Bond Theory.
- Define Co-ordination number.
- Write one example of each of ionisation, linkage and hydrated isomerism.
- Explain the formation of [Co(NH₃)₆]³⁺ ion on the basis of Valence bond theory. Convert the following: (a) acetic acid to ethyl acetate (b) acetic acid to ethyl alcohol.
10 20 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Chemical Reaction to Phenol to Cyclohexanol
Phenol can be converted into cyclohexanol by hydrogenation.
C₆H₅OH + 3H₂ → C₆H₁₁OH
(Phenol) → (Cyclohexanol)
10 00 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Chemical Reaction to Convert Phenol to Benzoquinone
Phenol can be converted into p-benzoquinone by oxidation.
Phenol + [O] → p-Benzoquinone
Chemical change:
C₆H₅OH → C₆H₄O₂
09 40 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Features of SN2 Mechanism
SN2 means Substitution Nucleophilic Bimolecular. It is a type of nucleophilic substitution reaction. Given below are the main features for your understanding:
- The reaction happens in a single step. There is no intermediate formed.
- The rate depends on both the alkyl halide and the nucleophile.
Rate = k [Alkyl halide][Nucleophile] - The nucleophile attacks from the opposite side of the leaving group.
- If the carbon is chiral, the product shows inversion. This is called Walden inversion.
- A high-energy transition state is formed where the carbon is partially bonded to both nucleophile and leaving group.
- Reactivity order:
Primary > Secondary >> Tertiary
Tertiary rarely undergo SN2 because of steric hindrance. - Strong nucleophiles like OH⁻, CN⁻, I⁻ favor SN2 needed.
09 20 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Aldol Condensation Reaction of Ethanal
The aldol condensation of ethanal is a reaction where two molecules of ethanal react in the presence of a dilute base to form a bigger molecule.
Step 1: Aldol Formation
When ethanal (CH₃CHO) is treated with dilute NaOH, two molecules combine to form a compound called aldol.
Reaction:
2 CH₃CHO → CH₃–CH(OH)–CH₂–CHO
The product formed is 3-hydroxybutanal, commonly called aldol.
This step is called aldol addition because:
- One molecule forms an enolate ion
- It attacks another ethanal molecule
- A β-hydroxy aldehyde is formed
Step 2: Condensation (On Heating)
When the aldol is heated, it loses a water molecule (dehydration).
CH₃–CH(OH)–CH₂–CHO → CH₃–CH=CH–CHO + H₂O
The final product is but-2-enal (crotonaldehyde).09 00 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
What is Reimer-Tieman reaction?
The Reimer-Tiemann reaction is a chemical reaction used to introduce a -CHO group (aldehyde group) into a phenol ring. It converts phenol into salicylaldehyde using chloroform and a base.
Reaction Conditions
- Reactant: Phenol
- Reagent: Chloroform (CHCl₃)
- Base: Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
- Medium: Basic medium
- Followed by: Acidic workup
General Reaction
Phenol + CHCl₃ + NaOH → o-hydroxybenzaldehyde (salicylaldehyde)
Example
When phenol reacts with chloroform in the presence of NaOH, an aldehyde group (-CHO) is introduced at the ortho position of the benzene ring.
Main product: Salicylaldehyde (o-hydroxybenzaldehyde)
Minor product: p-hydroxybenzaldehyde08 40 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Important 3/4-Mark/MCQ Questions of HCS Chemistry Solutions Chapter
- Derive the expression for molar mass of solute in terms of boiling point elevation of solvent.
- Explain the phenomenon of osmosis with a suitable diagram.
- Explain with the help of vapor pressure-temperature curves for solution and solvent, why boiling point of solvent is elevated when a nonvolatile solute is dissolved into it.
- What are non-ideal solutions? Explain with reasons and diagrams the positive and negative deviations from Raoult’s law shown by non-ideal solutions.
- Explain with vapor pressure-temperature curves that the freezing point of a solvent is lowered by dissolving a nonvolatile solute into it. Give a reason for such lowering of freezing of solvent. Definefollowing terms a) Reverse Osmosis b) Semi permeable membrane c) Osmotic pressure d) Isotonic solution.
08 20 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Important 2-Mark/MCQ Questions of HCS Chemistry Solutions Chapter
- For a very dilute solution, the osmotic pressure is given by π =?2 ??/? where V is the volume in L containing n2 moles of nonvolatile solute. Establish the equation for molar mass of solute.
- Distinguish between ideal and non-ideal solutions.
- Write two points to explain why vapor pressure of solvent is lowered by dissolving nonvolatile solute into it.
- In what way Kf and Kb are similar and in what way they are different?
- Calculate total moles after dissociation in 0.1M KCl solution and 0.05M aluminum sulphate solution.Which of the two solutions will have higher freezing point depression.
08 00 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Important 1-Mark/MCQ Questions of HCS Chemistry Solutions Chapter
- Sugar dissolves in water because..?
- The units of Henry’s law constant are..?
- Which of the following solutions /solvent has maximum vapor pressure?
- What are hypertonic solutions?
- What is cryoscopic constant?
- Write the effect of dissolution of a nonvolatile solute on the freezing point of solvent.
- Write the expression for relative lowering of vapor pressure.
07 40 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
HCS Chemistry BCC vs FCC Unit Cell
Basis of Comparison
BCC (Body-Centered Cubic)
FCC (Face-Centered Cubic)
Full Form
Body-Centered Cubic
Face-Centered Cubic
Arrangement of Atoms
8 atoms at corners + 1 atom at center
8 atoms at corners + 6 atoms at faces
Number of Atoms per Unit Cell
2
4
Coordination Number
8
12
Atomic Packing Factor (APF)
0.68 (68%)
0.74 (74%)
Packing Efficiency
Less dense
More dense
Edge Length Relation (r = atomic radius)
a = 4r / √3
a = 2√2 r
Structure Type
Not closely packed
Closely packed
Examples
Iron (Fe), Chromium (Cr), Tungsten (W)
Copper (Cu), Aluminum (Al), Silver (Ag), Gold (Au)
07 20 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
What is the “common ion effect”?
The common ion effect is when the ionization of a weak acid or weak base gets reduced because you add another substance that already has one of the same ions.
Simply put, if a solution already has a particular ion, adding more of the same ion makes the weak acid or base break apart less.
Take acetic acid for example. Its formula is CH₃COOH. In water, it breaks a little into:
CH₃COOH ⇌ CH₃COO⁻ + H⁺
Now, if you add sodium acetate (CH₃COONa) to this solution, it gives more CH₃COO⁻ ions.
Since CH₃COO⁻ is already present, the acid will break apart even less. This decrease in ionization is called the common ion effect.
07 00 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Few Important 3/4-Mark Questions on Solid State
- Calculate the packing efficiency for bcc lattice.
- In case of HCP structure, how are spheres in the first, second and third layers arranged?
- A substance crystallises in an fcc structure. The unit cell edge length is 367.8pm. Calculate the molar mass of the substance if its density is 21.5 g/cm3
- What are non-stoichiometric point defects? Explain with a diagram the formation of F-centres.
- Write the classification of stoichiometric point defects. What is a substitutional impurity defect? Explain solid solutions of metals and vacancies through aliovalent cations.
- Derive the relationship between the density of a substance, its molar mass and the unit cell edge length. Explain how you will calculate the number of particles and number of unit cells in x g of metal.
06 40 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Few Important 2-Mark Questions on Solid State
- Explain the terms: a) Isomorphism b) Polymorphism, with examples
- Classify the following solids as molecular, ionic, covalent and metallic solids. Pb, MgF2, SO2 and quartz
- Explain the vacancy defect with a diagram.
- Calculate the number of unit cells in 0.3 g of a species having a density of 8.5 g/cm3 and a unit cell edge length of 3.25×10-8 cm.
- When gold crystallises, it forms fcc unit cells. The unit cell edge length is 408 pm. Calculate the density of gold. Molar mass of gold is 197 g/mol.
06 20 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Few Important 1-Mark Questions on Solid State
- Write the effect on the density of a substance in the Frenkel defect?
- Write an example of a diamagnetic substance.
- Give one property common to both hcp and ccp crystal lattices.
- Write the relationship between the radius of the atom and the edge length of the fcc unit cell.
- Draw a diagram of bcc unit cell
06 00 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Enthalpy of Atomization (ΔH°atom)
Enthalpy of atomization is the amount of heat required to convert one mole of a substance in its standard state into its gaseous atoms.
- It is always positive because energy is absorbed.
- Units: kJ mol⁻¹
05 40 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Standard Enthalpy of Combustion (ΔH°c)
Standard enthalpy of combustion is the amount of heat released when one mole of a substance is completely burned in excess oxygen under standard conditions (298 K and 1 bar pressure).
- It is usually negative because heat is released.
- Units: kJ mol⁻¹
05 20 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Some Important 4-Mark Questions for HSC Chemistry
Q: (a) Distinguish between crystalline and amorphous solids.
(b) Explain bleaching action of chlorine in the presence of moisture.
Q: (a) Draw neat and labelled diagram of standard hydrogen electrode.
(b) Calculate e.m.f. of the following cell
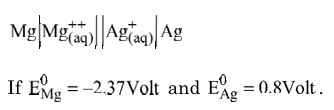
Q: (a) An element with molar mass 27 g/mol forms a cubic unit cell with edge length 405 pm. If the density of the crystal is 2.7 g cm–3, identify the type of unit cell.
(b) Derive the equation of Raoult’s law for a binary solution containing a non-volatile solute.
Q: (a) State whether entropy change is positive or negative in the following examples : (i) Melting of ice (ii) Vaporisation of a liquid
(b) Explain ‘common ion effect’ with example
05 00 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Chemistry Rate Constant (k)
Rate of reaction when concentration of each reactant is unity.
For first order:
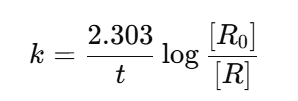
The unit depends on the order of reaction.
04 40 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Order of Reaction vs Molecularity
Basis
Order of Reaction
Molecularity
Definition
Sum of powers of concentration in rate law
Number of molecules in elementary step
Experimental?
Yes
No
Can be zero/fraction?
Yes
No
Applies to
Overall reaction
Only elementary step
04 20 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Very Important Formulas for HSC Chemistry Exam
Chemical Kinetics
First order equation:
k = (2.303 / t) log (a / a − x)Half-life (1st order):
t½ = 0.693 / kElectrochemistry
Nernst Equation:
E = E° − (0.0591 / n) log QGibbs Free Energy:
ΔG° = − nFE°Solutions
Raoult’s Law:
P₁ = X₁P₁°Relative lowering of vapour pressure:
(P° − P) / P° = X₂Solid State
Density of unit cell:
d = (Z × M) / (a³ × NA)04 00 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Chemistry Exam Prep Last Minute Tips
Below are some of the helpful tips for you to prepare for the upcoming chemistry exam, given by Armaann and Shivam. These two were among the toppers of HSC exam 2025:
- 90% of the paper is derived directly from the textbook. Ignore outside notes until you've mastered every "Exercise" and "Use Your Brain Power" box.
- Maintain a dedicated notebook for "Named Reactions" like Aldol Condensation and Reimer-Tiemann, as these are high-weightage and frequent favorites in Section D.
- Always write the "Given Data," the formula, and the final answer with correct units to ensure partial marks even if the calculation comes out to be wrong at the end.
- You can get easy marks by being thorough with definitions and formulas, as 25% of the paper is now dedicated to MCQs and Very Short Answers.
- Use a sharpened pencil for crystal lattices and electrochemical cells. Unlabeled or messy diagrams often result in zero marks.
03 40 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Some Important MCQ Questions for MAH HSC Chemistry
Q: Coordination number of atoms in bcc crystal lattice is _____.
A: 8Q: The unit of Henry’s Law constant is _____.
A: mol L–1 bar–1Q: pH of human blood is _____.
A: 7.4Q: Schottky defect is NOT observed in _____.
A: CsClQ: The freezing point of 0.1m aqueous solution of urea, if Kf for water is 1.86 K kg mol–1 is _____.
A: 0.186 ºC
Q: Ozone layer is depleted by _____.
A: chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)Q: Integrated rate law equation for a zero-order reaction is
A: [A] = [A]₀ - ktQ: The spin only magnetic moment of Fe²⁺ ion is ____.
A: 4.90 BMQ: The relation between radius of sphere and edge length in simple cubic lattice is ____.
A: r = a/203 20 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Maharashtra HSC Chemistry 2026 Expected Difficulty Level
The Chemistry exam for 2026 is expected to have an easy to moderate difficulty level, similar to the 2025 paper, which had easy objective and very short answers, moderate short answers, and easy-to-moderate long answers, with organic chemistry as the toughest section, followed by physical and inorganic.
03 00 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
HSC Chemistry Question-Wise Weightage
Section
Type of Questions
Number of Questions
Marks Allotted
A
Multiple Choice Questions
1 (has 10 subparts)
10
Very Short Answer Questions
1 (has 10 subparts)
8
B
Short Answer Questions
8 (attempt any 8 out of 12)
16 (2 marks each)
C
Short Answer Questions
8 (attempt any 8 out of 12)
24 (3 marks each)
D
Long Answer Questions
3 (attempt any 3 out of 5)
12 (4 marks each)
Total
31
70
02 40 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
HSC Chemistry Topics Forming 4-mark Questions
- Green Chemistry and Nanochemistry
- Environmental Chemistry
- Solid State Chemistry
- Electrochemistry
- Thermodynamics
- Organic Chemistry
- Coordination Chemistry
- p-Block Elements
- Solutions
- Chemical Kinetics
- Polymers
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
02 20 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
Maharashtra HSC Chemistry 2026 Chapter-Wise Weightage
Unit
Marks without Option
Marks with Option
Solid State
04
06
Solutions and Colligative Properties
05
07
Chemical Thermodynamics and Energetics
06
08
Electrochemistry
05
07
Chemical Kinetics
04
06
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
03
05
p-Block Elements
08
10
d and f – Block Elements
05
06
Coordination Compounds
03
04
Halogen Derivatives of Alkanes and Arenes
04
06
Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
04
06
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
05
07
Compounds Containing Nitrogen
04
06
Biomolecules
04
06
Polymers
03
04
Chemistry in Everyday Life
03
04
02 00 PM IST - 16 Feb'26
HSC Chemistry High-Weightage Topics
- Chemical Thermodynamics
- p-Block Elements
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Electrochemistry
- Chemical Kinetics
04 00 AM IST - 16 Feb'26
What are monosaccharides?
Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates which cannot be hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate units. They are basic building units of carbohydrates.
They are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones containing one aldehyde group or one ketone group along with multiple hydroxyl groups.
They are also called simple sugars.
General formula:
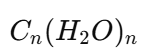 , where n ranges from 3 to 7
, where n ranges from 3 to 7Examples: Glucose, fructose, and ribose.
Monosaccharides are sweet in taste, soluble in water, and are reducing sugars.













