Updated By Puja Dey on 22 Jul, 2025 05:24
Registration Starts On February 04, 2026
Tell us your NEET score & access the list of colleges you may qualify for!
Predict My CollegeNEET Chemistry Syllabus PDF is released by the National Testing Agency (NTA) in the information booklet. In 2024, massive changes have taken place in the NEET syllabus of Chemistry. Some of the topics deleted from the NEET Chemistry syllabus include Hydrogen, Environmental Chemistry, Polymers, and Chemical Thermodynamics. On the other hand, few new chapters like Chemical Bonding, Chemical Kinetics, Chemical Thermodynamics, and many more. The Medical Council Committee curates the official NEET UG Chemistry Syllabus 2026 to match the educational demands of the current times.
Useful Links:
NEET 2026 Exam is expected to be conducted in the 1st week of May 2026. It is crucial for the applicants to understand the NTA NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026 to score good marks on the test. There were not many changes introduced in the NEET Chemistry Syllabus for 2026. The Chemistry Syllabus for NEET will aid students in identifying the important chapters for the exam. The NEET UG 2026 Chemistry Syllabus includes topics from both Class XI and XII NCERT Books. Read the article below to learn more about the NEET 2025 Chemistry Syllabus, important topics included, and latest update.
Get real time exam experience with full length mock test and get detailed analysis.
Attempt nowNEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026 has been declared by NTA, and no significant changes have been made from the previous year. Students must make sure that they are familiar with the official NEET Chemistry 2026 Syllabus to score good marks in the exam. Interested applicants can download the NEET UG 2026 Syllabus for Chemistry from the official website of NTA. Before discussing more in detail, let us take a look at the highlights of NEET Chemistry Syllabus PDF provided in the table below.
Particulars | Details |
|---|---|
Name of Event | NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026 |
Releasing Body | National Testing Agency |
Exam Name | NEET UG Exam 2026 |
Release Format | |
Release Mode | Online |
Total Number of Questions from Chemistry Subject | 50 Questions (45 to be attempted) |
Types of Questions | Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |
Sections in NEET 2026 Question Paper per Subject | Section A and Section B |
NEET Chemistry Section Number of Questions | 35 Compulsory Questions |
NEET Chemistry Section B Number of Questions | 15 Questions (Only 10 to be attempted) |
Total Marks | 180 marks (4 marks per question) |
NEET Chemistry Syllabus Weightage | 25% |
NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026 is divided into 3 parts - Organic, Inorganic, and Physical Chemistry chapters. Students will fnd the detailed NEET 2026 Chemistry Syllabus from the official website of NTA. It is important to note that the NEET Chemistry Syllabus for 2026 includes subjects from both Classes XI and XII NCERT Books. The chapters included from Class XI are Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry, Thermodynamics, and Equilibrium. The subjects from Class XII included in the chemistry syllabus of NEET 2026 are Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids, Chemical Kinetics, and Coordination Compounds. Students can refer to the table below for the direct download link of NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026 provided in the table below.
NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026 PDF(Direct Link) |
|---|
Also Check:
The NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026 - Physical, Inorganic and Organic. All the topics included in the chemistry syllabus of NEET UG 2026 is taken from the Class XI and XII topics from NCERT books. Students can refer to the table below to learn more about the Section wise NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026 discussed below.
There are 8 units in the Physical Chemistry Syllabus for NEET 2024 exam. The table below gives in-depth information regarding the topics included in each unit of the Physical Chemistry syllabus.
Unit No. | Unit Name | Topics |
|---|---|---|
1 | Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry |
|
2 | Atomic Structure |
|
3 | Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure |
|
4 | Chemical Thermodynamics |
|
5 | Solutions |
|
6 | Equilibrium |
|
7 | Redox Reaction and ElectroChemistry |
|
8 | Chemical Kinetics |
|
Also Read:NEET 2024 Chemistry Revision Notes
The Organic Chemistry syllabus for NEET 2024 exam consists of 9 units. Check out the table provided below for a detailed NEET 2024 syllabus for Organic Chemistry.
Unit No. | Unit Name | Topics |
|---|---|---|
1 | Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds | Purification - Crystallization. Sublimation, distillation, differential extraction, and chromatography - principles and their applications. Qualitative analysis - Detection of nitrogen, sulphur, phosphorus, and halogens Quantitative analysis (basic principles only) - Estimation of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, halogen, sulphur, phosphorus, calculations of empirical formula and molecular formulae: Numerical problems in organic quantitative analysis |
2 | Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry | Tetravalency of carbon: Shapes of simple molecules - hybridization (s and p): classification of organic compounds based on functional groups: and those containing halogens, oxygens, nitrogen and sulphur; Homologous series: Isomerism - structural and stereoisomerism. Nomenclature (Trivial and IUPAC) Covalent bond fission - Homolytic and heterolytic: free radicals, carbocations. and carbanions; stability of carbocations and free radicals. Electrophiles and Nucleophiles Electronic displacement in a covalent bond - Inductive effect, electromeric efl.ect. resonance. and hyperconjugation. Common types of organic reactions: Substitution, addition, elimination, and rearrangement. |
3 | Hydrocarbons | Classification, isomerism. IUPAC nomenclature, general methods of preparation, properties, and reactions. Alkanes - Conformations: Sawhorse and Newman halogenation of alkanes. projections (of ethane): Mechanism of Halogenation of Alkanes Alkenes - Geometrical isomerism: Mechanism of electrophilic addition: addition of hydrogen, halogens, water, hydrogen halides (Markownikoffs and peroxide effect): Ozonolysis and Polymerization Alkynes - Acidic character: Addition of hydrogen. halogens. water. and hydrogen halides: Polymerization. Aromatic hydrocarbons - Nomenclature, benzene - structure and aromaticity: Mechanism of electrophilic substitution: Halogenation, Nitration Friedelcraft's alkylation and acylation, directive influence of the functional group in mono-substituted benzene. |
4 | Organic Compounds Containing Halogens | General methods of preparation, properties, and reactions; Nature of C-X bond: Mechanisms of substitution reactions. Uses, Environmental effects of chloroform, iodoform, freons, and DDT |
5 | Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen | General methods of preparation, properties, reactions, and uses. Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Alcohols: Identification of primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols: mechanism of dehydration. Phenols: Acidic nature, electrophilic substitution reactions: halogenation. nitration and sulphonation. Reimer - Tiemann reaction Ethers: Structure Aldehyde and Ketones: Nature of carbonyl group; Nucleophilic addition to >C=O group, relative reactivities of aldehydes and ketones; Important reactions such as - Nucleophilic addition reactions (addition of HCN. NH3 and its derivatives), Grignard reagent; oxidation: reduction (wolf Kishner and Clemmensen); the acidity of a-hydrogen. aldol condensation cannizzaro reaction. Haloform reaction, Chemical tests to distinguish between aldehydes and Ketones. Carboxylic Acids Acidic strength and factors affecting it. |
6 | Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen | General methods of preparation. Properties, reactions, and uses. Amines: Nomenclature, classification structure, basic character, and identification of primary, secondary, and tertiary amines and their basic character. Diazonium Salts: Importance in Synthetic Organic Chemistry |
7 | Biomolecules | General introduction and importance of biomolecules Carbohydrates - Classification; aldoses and ketoses: monosaccharides (glucose and fructose) and constituent monosaccharides of oligosaccharides (sucrose, lactose, and maltose). Proteins - Elementary Idea of a-amino acids, peptide bond, polypeptides, proteins: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary Structure (qualitative idea only), denaturation of proteins, enzymes. Vitamins - Classification and functions. Nucleic Acids - Chemical constitution of DNA and RNA. Biological functions of nucleic acids. Hormones (General introduction) |
8 | Principles Related to Practical Chemistry | Detection of extra elements (Nitrogen, sulphur, halogens) in organic compounds; Detection of following functional groups; hydroxyl (alcoholic and phenolic), carbonyl (aldehyde and Ketones) carboxyl, and amino groups in organic compounds. The Chemistry involved in the preparation of the following: Inorganic compounds: Mohr's salt, potash alum. Organic compounds: Acetanilide, p-nitro acetanilide, aniline yellow, iodoform. The Chemistry involved in the titrimetric exercises - Acids, bases and the use of indicators, oxalic acid vs KMnO4. Mohr's salt vs KMnO4 Chemical principles involved in the qualitative salt analysis: cations - Pb2+. Cu2+. Al3*, Fe3+. zn2r, Ni2+, CA2+, Ba2, Mg2+. NH4+ Anions- CO32−, S2-, SO42-, NO3-, NO2-, Cl-, Br-, I- (Insoluble salts excluded) Chemical principles involved in the following experiments:
|
Candidates can also go through the NEET 2024 Most Important Topics to streamline their preparation and focus on key areas for a competitive edge in the exam.
The Inorganic Chemistry Syllabus for NEET 2024 consists of 4 units. Mentioned below are the names of topics from each.
Unit No. | Unit Name | Topics |
|---|---|---|
1 | Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties | Modern Periodic Law and present form of the periodic table. s, p, d and f block elements - periodic trends in properties of elements atomic and ionic radii, ionization enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy, valence. oxidation states. and chemical reactivity. |
2 | P Block Elements | Group -13 to Group 18 Elements General Introduction: Electronic configuration and general trends in physical and chemical properties of elements across the periods and down the groups; unique behavior of the first element in each group. |
3 | D and F Block Elements | Transition Elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence and characteristics, general trends in properties of the first.row transition elements - physical properties, ionization enthalpy, oxidation states, atomic radii, colour, catalytic behaviour, magnetic properties, complex formation, interstitial compounds, alloy formation; preparation, properties and uses of K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4. Inner Transition Elements: Lanthanoids- Electronic Configuration, Oxidation states and Lanthanide contractions. Actinoids- Electronic configuration and oxidation states. |
4 | Co-ordination Compounds | Introduction to coordination compounds, Werner’s theory; ligands, coordination number, denticity. Chelation; IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds, isomerism; Bonding-Valence bond approach and basic ideas of Crystal Field theory, colour and magnetic properties, Importance of coordination compounds (in qualitative analysis, extraction of metals and in biological systems) |
In the NTA NEET chemistry syllabus 2026, some of the high-weightage topics are p-block elements, coordination compounds, atomic structure, chemical equilibrium, etc. Here is the chapter-wise weightage of topics from the NEET Chemistry Syllabus.
Name of Chapter | Weightage | Total Questions Asked |
|---|---|---|
Physical Chemistry | ||
Atomic Structure | 3% | 1 |
Solutions | 4% | 2 |
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure | 6% | 2 |
Chemical Thermodynamics | 3% | 1 |
Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry | 2% | 1 |
Equilibrium | 4% | 2 |
Redox Reactions | 6% | 3 |
Chemical Kinetics | 4% | 2 |
Inorganic Chemistry | ||
Classification of Elements and Periodicity | 4% | 2 |
P Block Elements | 7% | 3 |
D and F Block Elements | 4% | 2 |
Coordination Compounds | 6% | 4 |
Organic Chemistry | ||
Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds | 2% | 1 |
Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen | 3% | 1 |
Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry | 5% | 2 |
Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen | 4% | 2 |
Hydrocarbons | 4% | 2 |
Organic Compounds Containing Halogens | 3% | 1 |
Biomolecules | 4% | 2 |
Principles Related to Practical Chemistry | 2% | 1 |
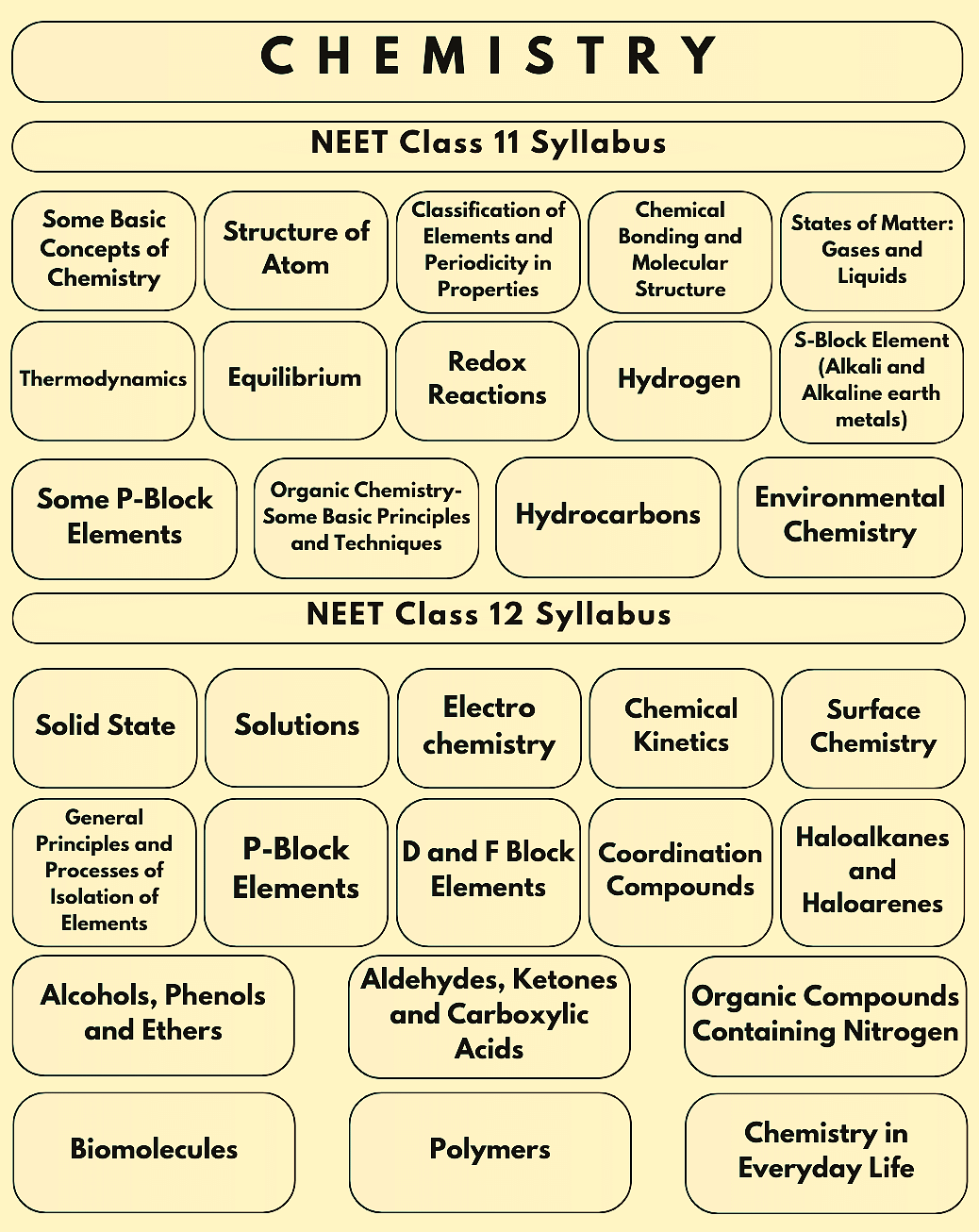
The Chemistry Syllabus for the NEET 2026 Exam consists of topics from the syllabus of class 11 and 12 NCERT Books. Check out the table below to gain insights on the class-wise syllabus for NEET Chemistry section and know How to Prepare Chemistry for NEET 2026, ensuring a thorough and effective study approach
NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026 from Class 11 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry | Some p-Block Elements | Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure | Redox Reactions |
Equilibrium | Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties | Thermodynamics | Hydrocarbons |
Structure of Atom | Organic Chemistry- Some Basic Principles and Techniques | - | - |
As discussed before, the NEET UG 2026 Chemistry syllabus contains topics from the Class XII curriculum of the CBSE board. Several questions are asked from the NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026 from Class 12, and hence applicants must prepare the topics with equal emphasis. Refer to the table below to learn more about the NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026 For Class 12.
NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026 from Class 12 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
ElectroChemistry | Solutions | Biomolecules | Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen |
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids | Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers | Haloalkanes and Haloarenes | Coordination Compounds |
d- and f-Block Elements | p-Block Elements | General Principles & Processes of Isolation of Elements | Chemical Kinetics |
NEET Chemistry syllabus 2025 consists of three parts namely physical chemistry, organic chemistry and inorganic chemistry. Some of the important topics in the NEET Chemistry 2025 syllabus are polymers, F-block elements, Equilibrium, Practical Chemistry etc. Students can check the details regarding important topics from the NEET Chemistry 2025 Syllabus given below.
Students can refer to the table below to learn about the important topics of physical chemistry from the NEET UG Chemistry Syllabus 2025.
Class 11 Chapters | Important Topics |
|---|---|
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry | Concentration Terms Relation Between Molarity and Normality Mole Concept Determination of Formula of Compound Stoichiometric Calculations |
Thermodynamics | P-V Work Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Capacity Thermochemistry |
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure | Covalent Character in Ionic Bonds Geometry or Shapes of Molecules General Introduction Polarity of Bonds Concept of Orbital Overlap in Covalent Bonds Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) |
Equilibrium | Expressing Hydrogen Ion Concentration Buffer Solution Solubility of Sparingly Soluble Salts Applications of Equilibrium Constant Equilibrium Constant Factors Affecting the State of Equilibrium |
Hydrocarbons | Stability of Alkene Chemical Reactions of Alkenes Aromatic Hydrocarbons Conformations of Hydrocarbons Isomerism in Alkenes Chemical Reactions of Aromatic Hydrocarbons |
Principles Related To Practical Organic Chemistry | Volumetric Analysis Qualitative Salt Analysis Enthalpy Analysis of Organic Compounds |
Students can refer to the table below to learn about the important topics of NEET UG Chemistry Syllabus 2025 from Class 12.
Class 12 Chapters | Important Topics |
|---|---|
Solutions | Colligative Properties Abnormal Molar Masses Solubility of Gases in Liquids Vapour Pressure of Liquid Solutions |
Amines | Aldehydes & Ketones: Reduction Reactions Carboxylic Acids Aldehydes & Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Aldehydes & Ketones: Oxidation Reactions |
Biomolecules | Disaccharides Proteins Glucose and Fructose Glucose: Reaction Due to Open Chain Structure Nucleic Acids |
Coordination Compounds | Coordination Compounds Isomerism in Coordination Compounds Ligands Werner’s Theory Bonding in Coordination Compounds |
The p-Block Elements Part 2 | Group-15 Elements Group-16 Elements Group-17 Elements Group-18 Elements |
Also Check: NEET 2025 Chemistry Question Papers.
There are several reactions, numericals, and formulas present in the NEET UG 2026 Syllabus of Chemistry. Hence, it is crucial to take proper strategies so that they can score good marks in the test. Here's how students can make sure they are ready.
Know What You Need to Study: Start by getting to know the NEET Chemistry syllabus 2026. Split it into sections like Physical Chemistry, Organic Chemistry, and Inorganic Chemistry.
Make a Study Schedule: Create a detailed plan that gives enough time to each topic based on how important it is and how well you know it. Break the syllabus into smaller parts and set achievable goals for each study session.
Use Good Materials: Use textbooks and online resources that are recommended for NEET preparation of NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026. Look for ones that explain things clearly and have practice questions to help you learn.
Focus on Understanding: Instead of just memorizing, try to understand why things work the way they do in Chemistry. This will help you solve problems and apply what you've learned in the exam.
Practice Regularly: Practice is key to mastering NEET 2026 Chemistry Syllabus. Spend time solving sample papers, past exam papers, and practice tests to get used to the exam format and improve your skills.
Review Often: Schedule regular review sessions to go over what you've learned and make sure you remember it. Make short notes summarizing important concepts to help you revise quickly.
Ask for Help: If you're stuck on something, don't be afraid to ask your teachers, mentors, or look for help online. It's important to clear up any confusion so you can keep moving forward.
Stay Updated: Keep an eye out for any changes to the NEET Chemistry syllabus or exam format. Stay connected to reliable sources of information so you don't miss anything important.
By following these steps and staying consistent, you can be well-prepared for the NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026.
Want to know more about NEET
Typical response between 24-48 hours
Get personalized response
Free of Cost
Access to community