The JEE Main syllabus 2026 syllabus comprises topics from Physics, Chemistry, Maths, Aptitude and Drawing for the respective programmes BTech/BE, BArch and BPlan. Check the JEE Main syllabus 2026 in detail on the page.
Tell us your JEE Main score & access the list of colleges you may qualify for!
Predict My CollegeJEE Main Syllabus 2026: The JEE Main syllabus has been divided into to sections for Paper 1 and Paper 2, which is further divided into subjects Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics for BE/BTech (Paper 1), whereas Paper 2A (BArch) comprises subjects Aptitude, Drawing and Mathematics, and Paper 2B (BPlan) comprises subjects Aptitude, Mathematics, and Planning.
The JEE Main Session 2 Physics syllabus 2026 comprises topics like Physics & Measurement, Kinematics, Laws of Motion, Gravitation, Work, Power & Energy, Thermodynamics, Optics, Oscillation & Waves and more.
The JEE Main Session 2 Chemistry Syllabus 2026 comprises topics like Atomic Structure, Basic Principles of Chemistry, Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure, Solutions, Equilibrium, and more.
The JEE Main Session 2 Maths Syllabus 2026 comprises topics like Sets, Relations, & Functions, Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations, Sequence and Series, Integral Calculus, Vector Algebra and more.
Candidates preparing for the JEE Main 2026 are advised to go through the JEE Main 2026 exam pattern along with the syllabus, as it will help the aspirants strategise their plan for cracking the JEE Main exam. Check the topic-wise detailed JEE Main syllabus below on the page.
Also Read
Get real time exam experience with full length mock test and get detailed analysis.
Attempt nowCandidates preparing for the JEE Main exam must go through the syllabus overview of the JEE exam. The overview will provide insights of the JEE exam pattern and syllabus:
JEE Main Syllabus Overview | |
|---|---|
Exam Conducting Authority | National Testing Agency (NTA) |
| |
JEE Main BE/BTech Syllabus |
|
JEE Main B Arch Syllabus |
|
JEE Main B Planning Syllabus |
|
| |
Q: Are the JEE Main syllabus and CBSE +2 syllabus the same?
A: The JEE Main syllabus and CBSE syllabus for classes 11 & 12 are overlapping. If you know the CBSE 10+2 syllabus and have gone through the NCERT books, you can easily score 250+ marks in the JEE Main exam.
Q: How much JEE Mains syllabus should I complete in 11th grade?
A: If you study well, you will be able to cover the 50% syllabus for the JEE Main exam 2025. The 11th-grade syllabus is for the basic concepts of the class 12 syllabus. It will help in solving and understanding the 12th and 12th syllabi.
Q: Has the syllabus changed for the JEE Main 2026 exam?
A: No, there is no change in the JEE Main syllabus 2026 yet. If any change occurs in the syllabus, NTA will notify through the official notification.
Q: Which mistake should I refrain from making while preparing for the JEE Main 2026 exam?
A: The first and foremost mistake that you should avoid is to target only the JEE Main preparation as approximately 14 lakh candidates take the exam and the difficulty level of the exam has increased in the last three years.
The JEE Main 2026 BE/ BTech syllabus has been divided into three subjects: Physics, Chemistry, and Maths. Each section in the exam will have 25 questions (20 Questions in Section A and 5 Questions in Section B). The JEE Main BE/BTech exam will be conducted for three hours (180 minutes) and will hold a total mark of 300. The candidates must take note that the exam will have a negative marking scheme where 4 marks will be awarded for the correct answer, whereas 1 mark will be deducted for the incorrect answer. However, there is no deduction for unattempted questions. Candidates can check the detailed syllabus for the JEE Mains Subject Wise Syllabus below on the page. The subject-wise syllabus will comprise
Candidates preparing for the exam must check the topic-wise detailed JEE Main 2026 physics syllabus below:
Unit | Topics |
|---|---|
Unit 1: Physics & Measurement |
|
Unit 2: Kinematics |
|
Unit 3: Laws of Motion |
|
Unit 4: Work, Power and Energy |
|
Unit 5: Rotational Motion |
|
Unit 6: Gravitation |
|
Unit 7: Properties of Solids & Liquids |
|
Unit 8: Thermodynamics |
|
Unit 9: Kinetic Theory of Gases |
|
Unit 10: Oscillations and Waves |
|
Unit 11: Electrostatics |
|
Unit 12: Current Electricity |
|
Unit 13: Magnetic Effect of Current & Magnetism |
|
Unit 14: Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents |
|
Unit 15: Electromagnetic Waves |
|
Unit 16: Optics | Optics chapter below:
Wave Optics
|
Unit 17: Dual Nature of Matter & Radiation |
|
Unit 18: Atoms & Nuclei |
|
Unit 19: Electronic Devices |
|
Q: Are questions asked from H.C. Verma in the JEE Mains Exam?
A: There will be no direct questions from the book H.C. Verma for Physics in the JEE Main 2025 exam. However, the questions will be based on the concepts and types provided in the book.
Q: What are the important topics in JEE Main Physics Syllabus 2026?
A: Some of the important JEE Main Physics syllabus 2026 are Current Electricity, Kinematics, Modern Physics, and Alternating Curren
The JEE Mains Chemistry syllabus 2026 is divided into 3 sections: Physical Chemistry, Inorganic Chemistry, and Organic Chemistry, which will contain numerical and theoretical questions. Check the sections wise JEE Mains 2025 Chemistry syllabus below.
Candidates can check the detailed JEE Main Physical Chemistry syllabus 2026 below:
Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry
Atomic Structure
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Kossel – Lewis approach to chemical bond formation, the concept of ionic and covalent bonds.
Ionic Bonding: Formation of ionic bonds, factors affecting the formation of ionic bonds; calculation of lattice enthalpy. Covalent Bonding: Concept of electronegativity. Fajan’s rule, dipole moment: Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR ) theory and shapes of simple molecules. Quantum mechanical approach to covalent bonding: Valence bond theory – its important features, the concept of hybridization involving s, p, and d orbitals; Resonance. Molecular Orbital Theory – Its important features. LCAOs, types of molecular orbitals (bonding, antibonding), sigma and pi-bonds, molecular orbital electronic configurations of homonuclear diatomic molecules, the concept of bond order, bond length, and bond energy. Elementary idea of metallic bonding. Hydrogen bonding and its applications.
Chemical Thermodynamics
Solutions
Equilibrium
Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
Chemical Kinetics
Check the JEE Main Organic Chemistry syllabus 2026 below:
Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry:
Alcohols
Ethers: Structure.
Organic Compounds containing Nitrogen
General methods of preparation. Properties, reactions, and uses
Amines
Biomolecules
Principles Related to Practical Chemistry
The chemistry involved in the preparation of the following:
Candidates can check the JEE Main Inorganic Chemistry syllabus 2026 below:
Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
p-block elements
Group -13
Group -14
Group -15
Group -16
Group-17
d- and f-block elements
Lanthanoids – Electronic configuration, oxidation states, and lanthanoid contraction
Actinoids – Electronic configuration and oxidation states.
Coordination Compounds
Q: Are alkyl halides part of the JEE Main 2026 Chemistry syllabus?
A: Yes, the alkyl halides are part of the JEE Main Chemistry syllabus 2026, and questions will be asked about the topic.
Q: What are the high-scoring topics in JEE Main Chemistry syllabus 2026?
A: Some of the high-scoring topics in the JEE Main 2026 Chemistry syllabus are Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen, Equilibrium, Chemical Kinetics, Transition Elements (D and F Block), Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure, Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry, and Coordination Compounds.
Also Read: JEE Main Best Books
The JEE Main Mathematics Syllabus comprises 2 sections A and B, where section A consists of MCQs, and Section B comprises Numerical Value Questions. Section A contains negative markings. Candidates can check the mathematics syllabus here from the below table.
Unit 1: Sets, Relations and Functions
The Unit 1 of JEE Main Maths syllabus comprises topics from chapter Sets, Relations and Functions. Check the detailed JEE Mains Maths syllabus for Unit 1 below:
Unit 2: Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
The Unit 2 of JEE Main Maths syllabus comprises topics from Chapter Complex Number and Quadratic Equation. Check the detailed JEE Mains Maths syllabus for Unit 2 below:
Unit 3: Matrices and Determinants
The Unit 3 of the JEE Main Maths syllabus comprises topics from Chapter Matrices and Determinants. Check the detailed JEE Mains Maths syllabus for Unit 3 below:
Unit 4: Permutation and Combination
The Unit 4 of the JEE Main Maths syllabus comprises topics from Chapter Permutation and Combinations. Check the detailed JEE Mains Maths syllabus for Unit 4 below:
Unit 5: Binomial Theorem and its Simple Applications
The Unit 5 of the JEE Main Maths syllabus comprises topics from Chapter Binomial Theorem and its Simple Applications. Check the detailed JEE Mains Maths syllabus for Unit 5 below:
Unit 6: Sequence and Series
The Unit 6 of the JEE Main Maths syllabus comprises topics from Chapter Sequence and Series. Check the detailed JEE Mains Maths syllabus for Unit 6 below:
Unit 7: Limit, Continuity and Differentiability
The Unit 7 of the JEE Main Maths syllabus comprises topics from Chapter Limit, Continuity, and Differentiability. Check the detailed JEE Mains Maths syllabus for Unit 7 below:
Unit 8: Integral Calculus
The Unit 8 of the JEE Main Maths syllabus comprises topics from Chapter Integral Calculus. Check the detailed JEE Mains Maths syllabus for Unit 8 below:
Unit 9: Differential Equations
The Unit 9 of the JEE Main Maths syllabus comprises topics from Chapter Differential Equations. Check the detailed JEE Mains Maths syllabus for Unit 9 below:
Unit 10: Coordinate Geometry
The Unit 10 of the JEE Main Maths syllabus comprises topics from Chapter Coordinate Geometry. Check the detailed JEE Mains Maths syllabus for Unit 10 below
Straight line
Circle, conic sections
Unit 11: Three Dimensional Geometry
The Unit 11 of the JEE Main Maths syllabus comprises topics from Chapter Three Dimensional Geometry. Check the detailed JEE Mains Maths syllabus for Unit 11 below:
Unit 12: Vector Algebra
The Unit 12 of the JEE Main Maths syllabus comprises topics from Chapter Vector Algebra. Check the detailed JEE Mains Maths syllabus for Unit 12 below:
Unit 13: Statistics and Probability
The Unit 13 of the JEE Main Maths syllabus comprises topics from Chapter Statistics and Probability. Check the detailed JEE Mains Maths syllabus for Unit 13 below:
Unit 14: Trigonometry
The Unit 14 of the JEE Main Maths syllabus comprises topics from Chapter Trigonometry. Check the detailed JEE Mains Maths syllabus for Unit 14 below:
Q: Will functional equations be asked in the JEE Main 2026 exam?
A: Yes, functional equations are one of the important topics for the JEE Main Maths syllabus. The question from the functional equations is asked frequently in the JEE exam. In the previous session, 2 questions were asked in the JEE Main exam.
Q: Is the solution of triangles studied for the JEE Main exam?
A: No, the solution of triangles is part of the JEE Advanced syllabus; it is not needed to study for the JEE Mains exam. However, if you want to prepare for the JEE Advanced 2026, you have to go through the solution of triangles.
Candidates can download the JEE Main syllabus PDF from the official website: jeemain.nta.nic.in. The steps to download the JEE 2026 syllabus are provided below with an image for the ease of candidates:
Step 1: Go to the official website: jeemain.nta.nic.in
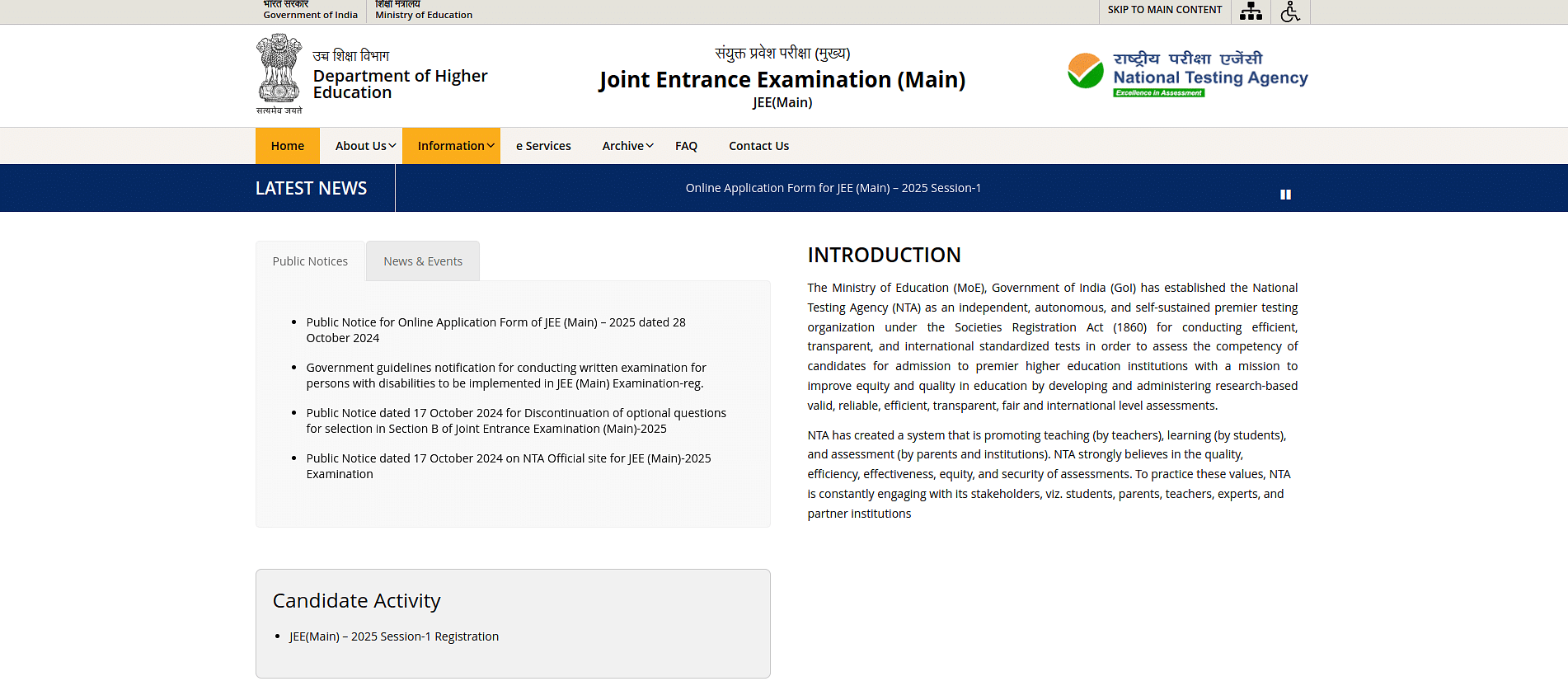
Step 2: Click on the ‘Information’ tab available on the website and click on the syllabus link from drop-down menu
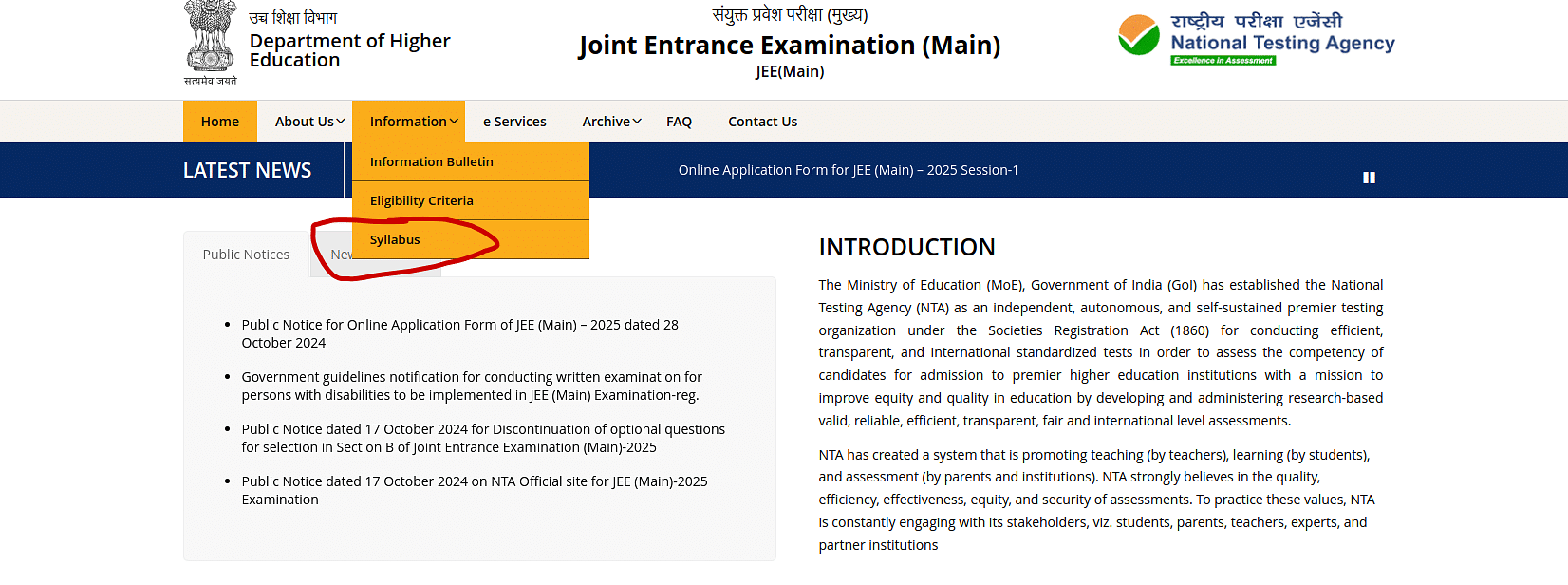
Step 3: Click on the JEE Mains Syllabus link available on the website
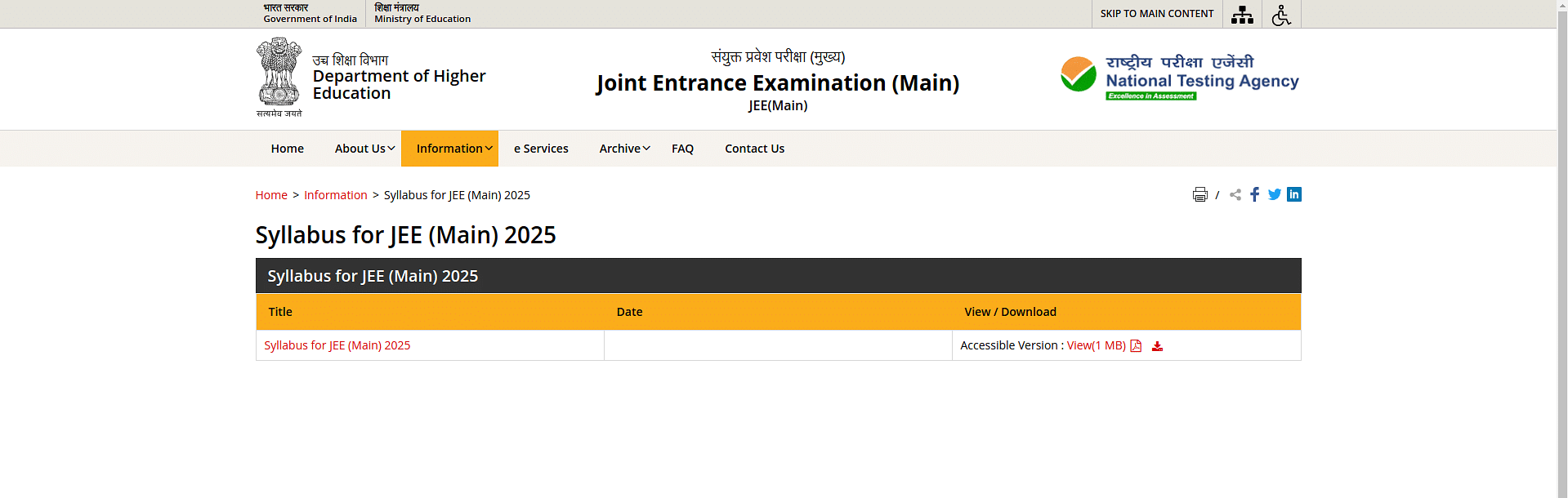
Step 4: The NTA JEE Mains syllabus will appear on the screen

Step 5: Download the JEE syllabus PDF and save it for later use
Candidates can check the respective 2A and 2B paper syllabus here.
The JEE Main syllabus Paper 2A is divided into Mathematics, Aptitude Test & Drawing Test. The Mathematics section is similar to Paper 1. Candidates will need to bring pencils, colour pencils, and crayons for this examination.
Sections | Topics |
|---|---|
Aptitude Test | Awareness - persons, buildings, materials, objects - Texture related to architecture; - Visualising three-dimensional objects from two-dimensional drawings - Analytical reasoning mental ability |
Aptitude Test |
|
Drawing Test | Sketching of scenes and activities from memory of urban landscape (public space, market, festivals, street scenes, monuments, recreational spaces, etc.), landscape (river fronts, jungles, trees, plants, etc.), and rural life. |
Candidates willing to attempt JEE Main Paper 2B can check the syllabus here. Paper 2B consists of Mathematics, Aptitute and Planning. The mathematics section is similar to that of Paper 1 whereas the aptitude is the same as B.Arch.
Sections | Topics |
|---|---|
General Awareness | General knowledge questions regarding prominent cities, government programs and development issues |
Social Science |
|
Thinking Skills | Map reading skills, Comprehension, scale, distance, direction, graphs and tables, basic concepts of statistics and quantitative reasoning |
The candidates can check the JEE Main syllabus PDF download links below in the table. Candidates merely have to click the download links for the JEE Main subject wise syllabus, and the PDF will be ready for download:
JEE Main Syllabus PDF | |
|---|---|
JEE Main 2026 Syllabus PDF | |
Candidates who are going to appear for the JEE Main 2026 exam must go through the detailed new exam pattern. According to the new revised syllabus, section B for every subject will hold only 5 compulsory questions instead of 10 optional questions. Also, the time duration for the PwD candidates has been increased by the NTA. The PwD candidates with benchmark disability candidates will be given 4 hours (240 minutes to complete the exam, and the PwD candidates can also demand scribe to take the exam; however, they have to inform the exam authority while filling out the application form. Check the detailed JEE Main exam pattern 2026 in the table below:
Paper | Sections | Marks | Time Durations |
|---|---|---|---|
Paper 1 (B.Tech/B.E) | Section A: MCQs
| 300 Marks | 180 Minutes (3 Hours) |
Section B: NATs
|
Canddidates who are preapring for the JEE Main Paper 1 exam must be acquianted with the exam pattern as well. The detailed exam pattern for JEE Main Paper 1 has been provided below in the table:
JEE Main Exam Pattern B.Arch & B. Plan | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Paper 2A ((BArch) | Section A: MCQs Maths Aptitude Drawing | 400 Marks | 180 Minutes (3 Hours) |
Section B: NATs Maths | |||
Paper 2B (BPlan) | Section A: MCQs Maths Aptitude Planning | 400 Marks | 180 Minutes (3 Hours) |
Section B: NATs Maths | |||
The JEE Main Syllabus with Weightage varies and aspirants need to have a thorough understanding of the topics and the expected number of questions or marks to prepare effectively for the exam.
Here is a list of topics and expected chapter-wise weightage for JEE Main Physics syllabus -
Topics | No. of Questions | Weightage |
|---|---|---|
Current Electricity | 3 | 9.9% |
Modern Physics | 2 | 6.6% |
Wave Optics | 2 | 6.6% |
Centre Of Mass | 2 | 6.6% |
Rotational Dynamics | 2 | 6.6% |
Work, Energy, and Power | 2 | 6.6% |
Laws of Motion | 2 | 6.6% |
Kinetic Theory of Gases & Thermodynamics | 2 | 6.6% |
Kinematics | 2 | 6.6% |
Magnetic Effect of Current and Magnetism | 2 | 6.6% |
Alternating Current | 2 | 6.6% |
Semiconductors | 1 | 3.3% |
Communication Systems | 1 | 3.3% |
Circular Motion | 1 | 3.3% |
Electromagnetic Waves | 1 | 3.3% |
Elasticity | 1 | 3.3% |
Error in Measurement | 1 | 3.3% |
Simple Harmonic Motion | 1 | 3.3% |
Sound Waves | 1 | 3.3% |
Electrostatics | 1 | 3.3% |
Capacitors | 1 | 3.3% |
The topics and JEE Mains chapter wise weightage for Chemistry have been provided below -
Topics | No. of Questions | Weightage |
|---|---|---|
Transition Elements & Coordination Compounds | 3 | 9.9% |
Periodic table, s and p-Block Elements | 3 | 9.9% |
Nuclear & Environmental Chemistry | 2 | 6.6% |
Thermodynamics & the Gaseous State | 2 | 6.6% |
Chemical And Ionic Equilibrium | 2 | 6.6% |
Solid-State And Surface Chemistry | 2 | 6.6% |
Atomic Structure | 2 | 6.6% |
Chemical Bonding | 2 | 6.6% |
Carbohydrates, Amino-Acids, and Polymers | 1 | 3.3% |
Aromatic Compounds | 1 | 3.3% |
Alkyl Halides | 1 | 3.3% |
Carboxylic Acids & their Derivatives | 1 | 3.3% |
Stereochemistry | 1 | 3.3% |
Hydrocarbon | 1 | 3.3% |
Solution & Colligative Properties | 1 | 3.3% |
General Organic Chemistry | 1 | 3.3% |
Electrochemistry | 1 | 3.3% |
Chemical Kinetics | 1 | 3.3% |
Mole Concept | 1 | 3.3% |
Redox Reactions | 1 | 3.3% |
Take a look at the list of topics and JEE Mains chapter wise weightage Physicshere to prepare well for the examination -
Topics | No. of Questions | Weightage |
|---|---|---|
3-D Geometry | 2 | 6.6% |
Determinants | 2 | 6.6% |
Sequences & Series | 2 | 6.6% |
Straight Lines | 2 | 6.6% |
Hyperbola | 1 | 3.3% |
Parabola | 1 | 3.3% |
Ellipse | 1 | 3.3% |
Maxima and Minima | 1 | 3.3% |
Statistics | 1 | 3.3% |
Vectors | 1 | 3.3% |
Quadratic Equations | 1 | 3.3% |
Trigonometric Equations | 1 | 3.3% |
Definite Integration | 1 | 3.3% |
Differential Equations | 1 | 3.3% |
Differentiability | 1 | 3.3% |
Indefinite Integration | 1 | 3.3% |
Binominal Theorem | 1 | 3.3% |
Limits | 1 | 3.3% |
Probability | 1 | 3.3% |
Complex Numbers | 1 | 3.3% |
Sets | 1 | 3.3% |
Permutations & Combinations | 1 | 3.3% |
Candidates can find the important topics for JEE Main exam from the below table
JEE Main Subjects | Important Topics |
|---|---|
Physics |
|
Chemistry |
|
Mathematics |
|
Unlock Your Results: Answer Key Available for Download
The JEE Main 2025 latest syllabus is available on the JEE Main official website: jeemain.nta.nic.in. The latest syllabus for the JEE Main 2025 exam was released on October 29, 2024.
The JEE Main syllabus has been reduced for the JEE Chemistry. The p-block elements have been divided into two parts: Group 13 to 17 and Group 18, whereas the chapters Environmental Chemistry and Coordination Compunds are merged into a single chapter.
The JEE Main syllabus 2025 has not been revised for the upcoming session 2025-26 by the National Testing Agency (NTA) yet. However, if any change occurs in the JEE syllabus, then NTA will release a prior notification related to the change in JEE Main 2025 syllabus. The latest NTA JEE syllabus for the exam is provided in the information brochure 2025.
The JEE Main 2025 syllabus has been released by the NTA (National Testing Agency) on October 29, 2024. The JEE Main syllabus has been released as a PDF along with the Information Brochure on the official website: jeemain.nta.nic.in. The candidates can download the syllabus by following the steps given below:
The JEE Main BArch syllabus 2025 has been divided into three sections Maths, Aptitude, and Drawing. The JEE Main Maths syllabus comprises topics from Integral Calculas, Differential calculas, Sets, Permutations and combinations, etc. whereas the JEE Main Aptitude comprises topics like Awareness of persons. Buildings, Materials, 3D- Perception and Appreciation of scale and proportion of Objects, Visualizing 3D Objects from 2D drawings, etc. and the Drawing sections comprise topics like Elevation of object rotation, Designing memory of urban scenes, Generation of plan, 3D view of an object, rotation, etc.
The JEE Main BTech syllabus 2025 comprises topics from Physics, Chemistry, and Maths. The Physics section comprises topics like Gravitation, Kinematics, Laws of Motion, Rotational Motion, etc. whereas the JEE Main Chemistry section comprises topics like basic Concepts of Chemistry, Chemical Thermodynamics, Solutions, etc. and the Maths syllabus comprises topics like Integral Calculas, Differential Calculas, Sets, Determinants, etc. The candidates must take note that the syllabus for the JEE Main Bachelor of Engineering is the same as the JEE Main Bachelor of Technology. Check the detailed JEE Main syllabus 2025 on the CollegeDekho page for JEE Main Syllabus.
Yes, the syllabus of JEE Main 2025 is the main source upon which preparation should be made. The questions that are asked in the JEE Main question paper are topics taken from the syllabus.
No, the JEE Main syllabus 2025 is not released officially at jeemain.nta.nic.in.
JEE Main 2025 Paper 1 syllabus includes Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics courses that must be studied for the BTech entrance test. Nevertheless, for Paper 2A (BArch), applicants must prepare their aptitude learning and sketching abilities. Topics from General Awareness, Social Science, and Thinking Skills must be examined for Paper 2B (BPlan).
The JEE Main syllabus 2025 is comparable to the CBSE Class 11 and 12 curriculum, but students must study for JEE Main using the NTA syllabus. Candidates should keep in mind, however, that the level of questions in JEE Main is comparable to the level of questions posed in classes 11 and 12.
The JEE Main 2025 syllabus includes topics from Class 11 and 12. As a result, several chapters from Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics become equally important for both Boards and the JEE Main Exam from both classes.
Typical response between 24-48 hours
Get personalized response
Free of Cost
Access to community