- Levels for Police Ranks in India
- Order wise Police Rank List in India with Insignia & …
- All Police Ranks in India in Detail
- Salary of Different Indian Police Ranks
- Police Rank List in Commissionerate System of Policing
- What is the Highest Police Rank in India?
- Two-Star Police Ranks In India
- Three-Star Police Ranks in India
- Faqs

Police ranks in India in order of hierarchy start with DGP and end with Constable.In each state of India, the government is responsible for appointing police officers and also for appointing the powers that apply to the police ranks in their respective states. The state government defines the Indian police ranks by the legislatures and the rules. However, in the union territories, the Central government is responsible for controlling the police post list and salary through lieutenant governors of the union territories. The union government also has the power to establish any particular order regarding the police rank list in India if there is an emergency. Read on to find all about the police rank list in India and the different Indian police ranks.
Also Read: How to Become a Police Officer?
Levels for Police Ranks in India
The candidates for Indian Police ranks are recruited at four different levels:
- Constabulary
- Upper Sub-ordinate
- SPS (through the State Public Service Commission)
- IPS ( through Union Public Service Commission)
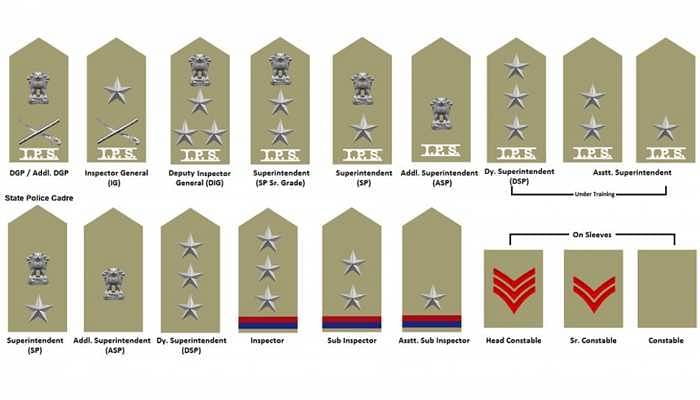
Order wise Police Rank List in India with Insignia & Stars
There is a proper hierarchy that the Indian government follows to recruit the police ranks in India. Check out the rank-wise Indian police ranks and badges from the table given below:
Ranking | Police Rank (Lowest to Highest) | Stars on Uniform | Badge |
|---|---|---|---|
15 | Constable | No Star | |
14 | Lance Naik/ Havaldar | No Star - Single Strip |  |
13 | Havaldar/ Senior Constable | No Star - Three Strips | |
12 | Head Constable/Assistant Sub-Inspector (ASI) | One Star, One Red Strip and One Blue Strip | |
11 | Sub-Inspector (SI) | Two Star, One Red Strip and One Blue Strip | |
10 | Inspector | Three Star | |
9 | Deputy Superintendant of Police (Dy. SP) | Three Star, One Red Strip and One Blue Strip |  |
8 | Assistant Superintendent of Police (ASP) | Three Star & IPS Badge | |
7 | Additional Superintendent of Police (ASP) | Ashok Emblem & IPS Badge | |
6 | Superintendent of Police (SP) | Ashok Emblem, One Star & IPS Badge | |
5 | Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP) | Ashok Emblem, Two Star & IPS Badge | |
4 | Deputy Inspector General of Police (DIG) | Ashok Emblem, Three Star & IPS Badge | |
3 | Inspector-General of Police (IG) | One Star, Cross Swords & IPS Badge | |
2 | Additional Director General of Police (ADG) | Ashok Emblem, Cross Swords & IPS Badge | |
1 | Director-General of Police (DGP) | Ashok Emblem, Cross Swords & IPS Badge |
All Police Ranks in India in Detail
Indian police service ranks are identical to the hierarchy of police machinery. How police rank in India are organised is given below.Constable Rank in Indian Police
Constable is the starting rank among Indian police ranks of the police hierarchy in India. It is also known as 'Sipahi' in some states. The constable is permissible to carry the rifle but arms training is given after the recruitment. The constable can become a senior constable and then they can become head constable with the event of promotion. There are three main positions here:
Constable
Senior Constable
Head Constable
Assistant Sub Inspector Rank in Indian Police Department
Assistant sub-inspector is recruited through competitive examinations which are conducted by the state governments for different Indian police ranks. Every state in India has its own recruitment process and competitive examinations for different positions from the police rank list in India. There are three main positions which are available in this rank:
Assistant Sub-Inspector of Police (ASI)
Sub-Inspector of Police (SI)
Inspector of Police (PI)
Provincial/State Police Service Officers (PPS/SPS) Ranks
The State Public Service Commission is responsible for recruiting the state police service officers and this is a gazette service. The people who have served this rank for a longer period can also be promoted to the Indian Police Service post. There are four main positions which are available to the people who will be appointed as a DSP by their state Public Service Commission:
Deputy Superintendent of Police (DSP)
Additional Superintendent of Police (ASP)
Superintendent of Police (SP)
Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP)
Police Ranks in India: IPS
If you want to apply for an IPS position then you will have to take a particular civil service examination and then you will be eligible to be appointed as the assistant superintendent if you have successfully passed the entrance examination. You can check out the positions available in the Indian police ranks after passing the civil services examination from the pointers given below:
Assistant Superintendent of Police
Additional Superintendent of Police
Superintendent of Police (SP)
Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP)
Deputy Inspector General of Police
Inspector-General of Police (IGP)
Additional Director General of Police
- Director-General of Police (DGP)
Salary of Different Indian Police Ranks
Check out the various Indian police ranks and salary per month for the entire police rank list in India provided in the table below.
Police Ranks in India | Average Salary |
|---|---|
Inspector General of Police (IG) | INR 17.50 LPA |
Director General of Police (DGP) | INR 14.30 LPA |
Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP) | INR 13.50 LPA |
Superintendent of Police (SP) | INR 10.60 LPA |
Additional Superintendent of Police (ASP) | INR 9 LPA |
Deputy Superintendent of Police (DSP) | INR 7 LPA |
Inspector | INR 6.50 LPA |
Sub-inspector | INR 5.30 LPA |
Head Constable | INR 4.20 LPA |
Constable | INR 3- 4 LPA |
Also Read: How to Prepare for IAS After 12th Board Exams
Police Rank List in Commissionerate System of Policing
The Police departments in India are under the jurisdiction of two different commands. When it comes to daily operations they work under the Superintendent of Police. However, the executive powers of the police department are vested in the District Magistrate who is responsible for overlooking the law and order of a particular city. Any warrants that the police department needs must be issued by the DM to arrest anybody because the powers to issue warrants and arms licenses are vested in the District Magistrate. Such a system often causes delays because the DM has various other responsibilities and obligations.
Some states resolve this issue by reorganizing the police forces of metropolitan and other important cities or districts into commissionerate systems, in which the commissioner of police also has executive authority to issue warrants Since the Police Commissioner is a DIG-level officer.
Police Rank in IG and Commissionerate System of Policing
There are some differences in the Police department ranks in the IG and Commissionerate system of policing. While the lower ranks in both systems are the same, differences in ranks arise at the level above the inspector rank, due to more powers in the Commissionerate system. Check the police hierarchy in the commissionerate system from the table given below.
Police Rank in IG Police System | Police Rank in Commissionarate Police System |
|---|---|
Director-General of Police (DGP) | |
Additional Director General of Police (ADG) | Commissioner of Police |
Inspector-General of Police (IGP) | Additional Commissioner of Police |
Deputy Inspector General of Police | Additional Commissioner of Police |
Senior Superintendent of Police | Deputy Commissioner of Police |
Superintendent of Police | Additional Deputy Commissioner of Police |
Additional Superintendent of Police | Additional Deputy Commissioner of Police |
Deputy Superintendant of Police (Dy. SP) | Assistant Commissioner of Police |
Inspector | |
Sub-Inspector | |
Assistant Sub-Inspector | |
Head Constable | |
Constable | |
Also Read: How to Prepare for UPSC Civil Services Personality Test
What is the Highest Police Rank in India?
In the police force, the highest position is that of Director-General of Police (DGP) who occasionally reports directly to the chief minister of the state and, in other cases, to the Chief Secretary of the state. One of the three All India Services (AIS) is the IPS, officially known as the Indian Police Service, where individuals are selected by UPSC and allocated to individual state governments. At the highest level of a state's policing framework is the IPS. Only IPS members become eligible for leadership positions in the police force. Go through the points below for more details on the highest police rank in India.The Director General of Police (DGP) is the highest police rank in India. IPS officers who have cleared civil services examination or appointed as DGP. The officers with at least 33 years of service are often considered for this position. You can also call the DGP “State Police Chief” because he is typically the head of state and Indian police ranks. Check more information about the same here:
The DGP is appointed by the cabinet and they hold a 3-star rank.
There may also be other officers from the police rank list in India who hold the rank of DGP in the state.
The rank insignia of a Director General of Police or Commissioner of Police (in Delhi) is the national emblem over crossed sword and baton.
These officers wear Gorget patches on their collar which have a dark blue background with an oak leaf pattern stitched on it.
They are appointed by the state government in consultation with the UPSC.
Also Read: Best Graduation Subjects for IAS after 12th
Two-Star Police Ranks In India
In India, the rank of a police officer is represented by stars, with a higher number of stars indicating a greater level of responsibility and power. A Sub-Inspector (SI) is assigned two stars, while a Head Constable only has one star on their shoulder. The Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP), a senior rank in the Indian Police Service and state police services, is assigned two stars. The SSP rank is higher than that of a Superintendent of Police (SP) but lower than that of a Deputy Inspector General of Police (DIG).
Three-Star Police Ranks in India
Inspector rank and above are assigned three stars. As the rank goes higher, the Ashok Emblem replaces the stars, and as the hierarchy goes even higher, Swords are used instead. The rank of Deputy Inspector General of Police (DIG) is denoted by three stars on the shoulder board. DIG is a senior-ranking officer who is responsible for heading the police force of a state or a union territory. Their primary responsibilities include maintaining public order, overseeing law enforcement activities, and ensuring the safety and security of citizens within their jurisdiction. In the State Police Services, the rank of Deputy Superintendent of Police (DSP) is assigned three stars.
The police force of the country is responsible for maintaining law and order which is one of the biggest responsibilities to carry. The police officers are also responsible for the safety of the citizens. Hopefully, this article was able to inform students about the different Indian police ranks successfully.
Related Links:
IAS Toppers Who Cracked UPSC Civil Services in First Attempt |
Stay tuned with us for more articles related to police ranks and recruitment in India!





























Similar Articles
Top Institutes with 100% Job Placements in 2023-24: Highest Package, Key Recruiters
List of Colleges in Delhi University: Affiliated/ Recognised Colleges in DU
Best Career Options After Qualifying UGC NET 2024
What is a Good Score in UGC NET 2024?
UPSC CSE 2025: Calendar (Out), Posts, Strategy, Registration & More
How to Check KVS Admission List 2024-25 (1st, 2nd, 3rd): Direct Link, Latest Updates, Steps for Class 1 & Above